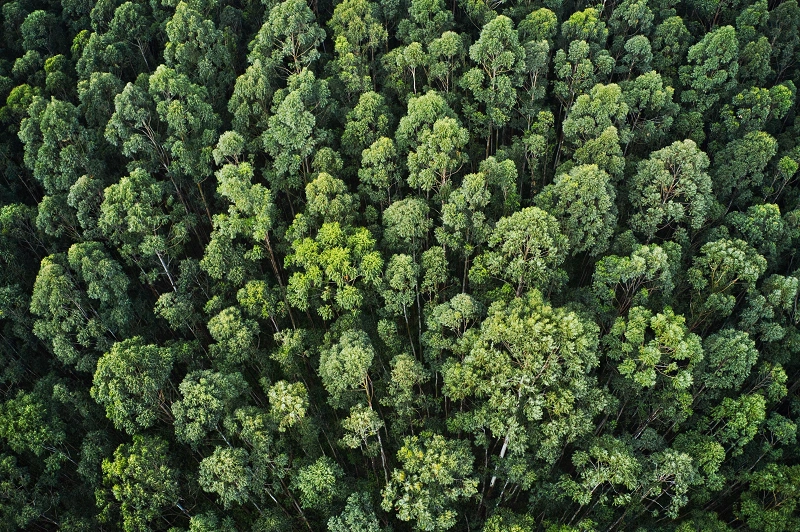
WHY ARE TREES IMPORTANT TO THE ENVIRONMENT?
Trees help purify the air we breathe, filter the water we drink, and provide habitat for over 80% of the world's biodiversity. Forests provide jobs for over 1.6 billion people, absorb harmful carbon from the atmosphere and are key ingredients in 25% of all medicines. Have you ever taken aspirin? It comes from the bark of a tree!
BIODIVERSITY
A tree can be home to hundreds of species of insects, fungi, mosses, mammals and plants. Depending on the type of food and shelter they need, different forest animals require different types of habitat. Without trees, forest creatures had nowhere to call.
- Young, open forests: These forests occur as a result of fires or logging. Shrubs, grasses, and young trees attract animals such as black bears, American goldfinches, and North American bluebirds.
- Middle-aged forests: In middle-aged forests, taller trees begin to outgrow weaker trees and vegetation. The open canopy allows for the growth of ground vegetation favored by animals such as salamanders, moose and tree frogs.
- Old-growth forests: With large trees, a complex canopy and highly developed vegetation, old-growth forests provide habitat for numerous animals, including bats, squirrels and many birds.
AIR
Trees help purify the air we breathe. Through their leaves and bark, they absorb harmful pollutants and release pure oxygen for us to breathe. In urban environments, trees absorb polluting gases such as nitrogen oxides, ozone and carbon monoxide and wash away particles such as dust and smoke. Rising levels of carbon dioxide caused by deforestation and the burning of fossil fuels trap heat in the atmosphere. Healthy, strong trees act as carbon sinks, offsetting carbon and reducing the effects of climate change.
Protection of trees